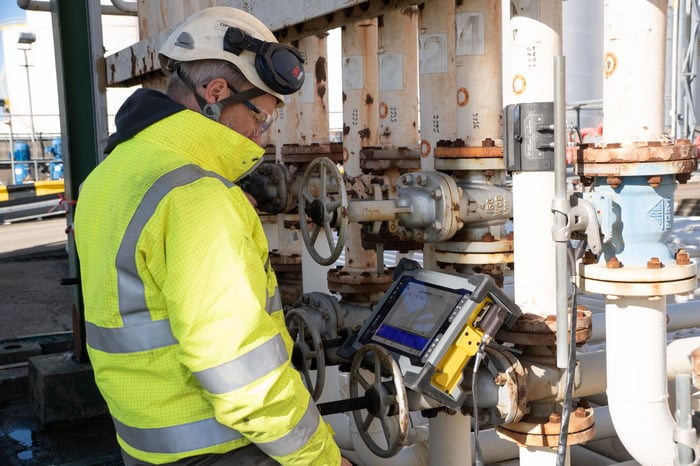
Dead leg inspections are crucial for ensuring the enduring reliability of pipeline systems, encompassing vital aspects such as safety, quality assurance, and environmental protection. Regulatory authorities, including the HSE, API, and EU-OSHA, outline explicit guidelines to uphold pipeline integrity. Compliance with these standards is not only a legal obligation but also a responsibility to safeguard the well-being of the workforce, the environment, and the public. Nevertheless, these dead-end sections have long posed a challenge for inspection.
The Enigma of Pipeline Dead Legs
Dead legs, often concealed from view, represent sections of pipelines that lead to nowhere or see infrequent use. They can vary in size and shape, from short stubs to extended branches, and are found across various industrial applications. Historically, dead legs have carried an elevated risk due to aggressive corrosion, leading to accelerated pipe wall thinning. Inspecting dead legs has been a formidable task due to limited accessibility and the unsuitability of conventional inspection methods for these confined spaces, potentially leading to inaccuracies and undetected defects.
A recent incident involving localized corrosion within a dead leg resulted in a catastrophic pipeline failure, releasing highly flammable material. Despite these risks, they have often received less attention than the mainline pipes.
The Long Game for Short Dead Legs: Overcoming Inspection Limitations
Eddyfi Technologies’ Sonyks® guided wave inspection equipment has emerged as a game-changing non-destructive testing (NDT) method for inspecting pipelines. This technology involves the transmission of ultrasonic waves along the length of the pipe, enabling the detection of corrosion and other piping defects. Historically, guided wave technology was primarily focused on long sections of pipelines due to the lower frequency ranges not being suitable for shorter sections of pipe.
The challenge of inspecting short dead legs persisted with their limited length and constricted space for wave propagation. Traditional guided wave tools faced limitations, and the frequencies used resulted in a dead zone, a region adjacent to the sensors that was impossible to inspect. This dead zone significantly impacted the suitability of guided wave technology for shorter pipe lengths.
Recent advancements in guided wave or long-range ultrasonic testing (LRUT) technology have centered on developing higher-frequency tools adaptable to the constrained space of short dead legs. These tools, pioneered by Eddyfi Technologies, employ shorter wavelengths, enhancing their effectiveness in inspecting even the tightest spaces. The use of higher frequencies not only reduces the dead zone but also improves resolution and sensitivity. See how MRUT is applied for small diameter pipe inspections here.
Benefits of Higher Frequency Tools: Unprecedented Precision
The new higher frequency magnetostrictive tools offer a multitude of advantages for inspecting short dead legs:
- Superior Precision: These tools excel in detecting small defects and anomalies in confined spaces, elevating inspection accuracy.
- Enhanced Safety: More accurate inspections improve risk assessment and hazard prevention, particularly in industries dealing with hazardous materials.
- Efficiency: Inspection of short dead legs can now be conducted more efficiently, reducing downtime during maintenance and inspections.
- Cost Savings: Addressing defects promptly results in reduced repair costs and extended pipeline lifespan.
The Future of Inspection with Guided Wave Technology for Short Dead Legs
With higher frequency sensors and advanced data collection techniques, Eddyfi Technologies’ Sonyks guided wave equipment is paving the way for a new era of short-length piping inspections. These tools are becoming indispensable for industries reliant on the safety and reliability of their pipelines.
Stay ahead of the curve by enrolling in our Eddyfi Academy courses available on guided wave testing.
The inspection of short dead legs, once a formidable challenge, has been revolutionized by Eddyfi Technologies' Sonyks guided wave system and its new higher-frequency tools. These advancements ensure the safety and reliability of pipelines and lead to cost savings and more efficient maintenance practices.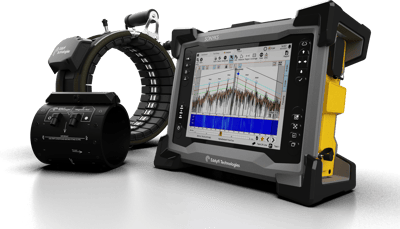
As industries continue to depend on pipelines for their operations, the ongoing development and application of guided wave technology in inspecting short dead legs will remain a critical factor in maintaining the integrity and safety of these vital networks.
Shop our entire guided wave testing offering online, and say goodbye to inspection dead ends thanks to Eddyfi Technologies Beyond Current solutions. Prefer to chat with an industry expert? Contact us for answers to your questions.






